Metabolite changes associated with earthworms (Eisenia fetida) graphene exposure revealed by matrix-
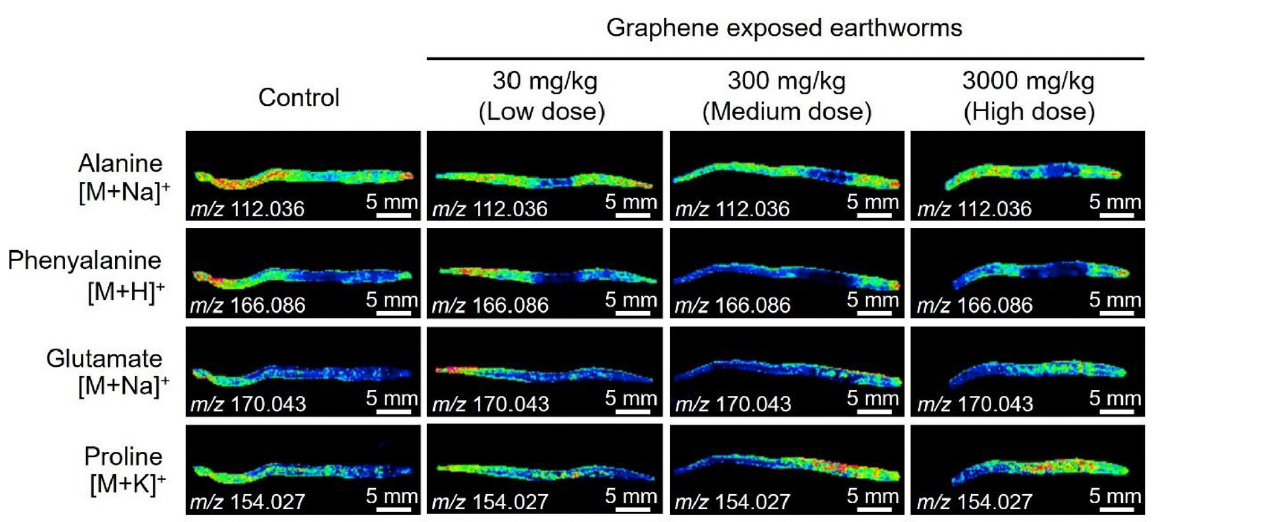
Abstract:The increased production and environmental release of graphene nanoparticles has raised concerns about its environmental impact, but the effects of graphene on living organisms at the metabolic level remain unknown. In this study, we used matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI)-based untargeted metabolomics to investigate the metabolic response of juvenile earthworms (Eisenia fetida) to graphene exposure in soil tests for the first time. Our results reveal that graphene-exposure significantly disturbs earthworm metabolome, and graphene toxicity on earthworm shows non-concentration-dependent effect. Alanine, phenylalanine, proline, glutamate, arginine, histidine, maltose, glucose, malate, succinate, myo-inositol, and spermidine were successfully screened as significantly change compounds in earthworms for the exposure of graphene. The heterogeneous distributions of these metabolites in earthworm were also clearly imaged by MALDI-MSI. Our MSI results fully showed that the metabolite expression levels in juvenile earthworms significantly changed (up-/down-regulation) after exposure to graphene nanoparticles. This work improves our understanding of graphene nanoparticle toxicity to juvenile earthworms and also enables the continued progression of MALDI-MSI-based metabolomics as an emerging, reliable, and rapid ecotoxicological tool for assessing contaminant toxicity.


